.jpg) |
| SERPs |
SERPs (= Search Engine Result Pages) show search results for a keyword or a combination of terms or keywords as snippets. They consist of a title, a short description, and a link or, depending on the length, an excerpt from the target link. Rich snippets add additional information to the result. The number of results in the search results varies. Usually, Google shows 10 snippets with the SERPs.
How are the SERP snippets structured?
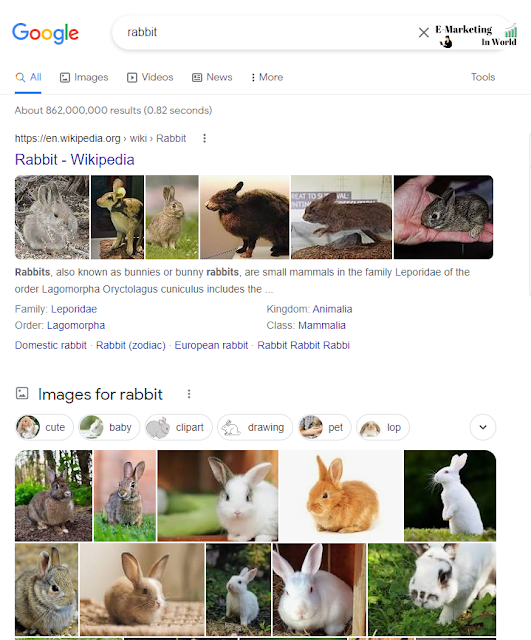
Search Engine Result Pages contain individual search engine results and consist of a title, a URL, and a description.
In some cases, so-called additional links are also included, which are below the actual fragment. These results look very similar across different search engines. The headline on Google, Bing, and Yahoo are blue, the URL is black, and the description is gray or black.
 |
| SERPs |
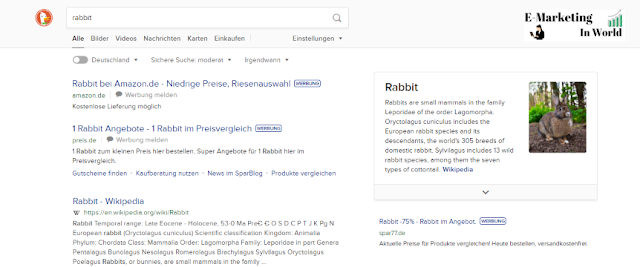
On the other hand, the slightly newer search engine DuckDuckGo doesn't use different colors and displays the result with a larger title, less description, and the URL of the result. The URL is shown here in green.
 |
| SERPs |
As mentioned above, Google can display snippets in several ways. However, there is a basic structure. A snippet usually includes the title of the webpage, the URL of the webpage, and a meta description, which is a short description.
So the snippet contains:
- Page title with 70 characters.
- URL (short).
- Meta description 156 characters.
Note, however, that Google and its algorithm can also use optimized snippets to retrieve the page content and reproduce it in the description if it better matches the search query.
How the SERPs are structured always depends on the keywords entered. As a rule, the SERPs contain regular search results and paid ads. The latter is at the top and bottom of the search results and is marked as advertising.
The snippets are displayed on the SERPs/search results pages in descending relevance as fragments of the search results.
Depending on the search query, in addition to the search result fragments, other formats enriched with additional information are also displayed.
For example, Google search results demonstrate the following:
Selected Fragments:
- Rich snippets
- questions and answers
- knowledge graph
- Job offers
- Local results
- Google My Business
- news
- App links (for mobile search).
The art of optimizing SERP snippets is to make the best use of the available space. Google offers you different amounts of space in the search results on desktop and mobile:
- In the title: 580 pixels (computer) or 920 pixels (mobile phone).
- In the description: 990 pixels (desktop) or 1300 pixels (mobile)
How should you structure your title, description, and URL?
The title should contain the most important keyword of the respective page and preferably rank as high as possible.
Then you can add a letter or USP ( Unique Selling Proposition ). You can also name your domain/company/brand.
These should be at the end of the header (except on the home page of your site) as it may fall short if it's too long. Also, a user who doesn't know your domain/company/brand may not necessarily be able to relate to it when it's upfront.
The title is short and about 55-63 characters long. You must comply with this restriction, otherwise, the title will be too long and will be truncated to "...".
It would be nice if you viewed your snippets not only on desktop but also on mobile as the title breaks there and hence the length can be different.
The description must contain the keyword or keyword or suitable synonyms in the SERPs so that the user can find his search query again.
It should keep the user interested in what is on the website. Also, the description should briefly describe the content so that the user knows what to expect and also makes him go to the page. This means that you must include a call to action at the end of the description.
Here, too, there is a certain length that you must adhere to avoid cropping the description. This is currently about 163 characters, but this changes from time to time. For the description, you should also look at the mobile SERPs so that the description is not truncated due to the limited space.
You can't manipulate the regular snippet URL, unlike the URL for AdWords sponsored ads. A speaking URL is an advantage here since the user is more likely to visit your website.
You must choose a title and description for each subpage of the website individually so that differences between distinct pages and their content matter. What you should definitely pay attention to is the correctness of the snippets.
After clicking the snippet, the user should find exactly what the snippet promised on the page.
Otherwise, the visitor will return to the search result and the bounce rate will increase. This is not a good signal for ranking and means your page should not rank high for the relevant search query.
If you are not able to manage individual meta tags for each page, you can have them generated automatically by specifying a specific format.
To make your work a little easier, you can also use SERP snippet generators such as those from Sistrix. Of course, there are other tools than Sistrix that offer something like XOVI, for example.
What do the displayed SERPs depend on?
When a user enters a keyword, they want an accurate answer as quickly as possible.
Therefore, most users click on one of the first fragments of the search engine results page instead of scrolling through the rest of the entries. This is also reflected in the number of clicks. The click rate drops significantly on the SERPs from the first to the second search result.
This clearly shows that the first page of the SERPs and a high position there are relevant.
According to the study, about 60% of users click on the first search result, compared to 17% on the second SERPs. With declining positions on the search engine results pages, the downward trend continues. Only a subset of users accesses the second page of the results list.
Accordingly, the pages on these SERPs are rarely clicked on. To bring the desired traffic to the first positions, website operators, therefore, try to place their site as high as possible in the search results.
This can be achieved with measures from the field of search engine optimization or with search engine advertising, i.e. Google Ads.
A web page's position on search engine results pages is not static.
If you display Google search results for a keyword, the order on the displayed SERPs can change in a very short time. But how does a search engine decide what information is important to the user?
The search engine algorithm uses fixed, partly secret criteria to evaluate the most relevant result for the user.
However, user-specific factors also affect the search results that are displayed. These include, for example:
- user location
- end device
- previous searches
From time to time, adjustments are made to the search engine algorithm, and evaluation criteria are added or changed. These updates can significantly change the ranking.
Consequently, constant monitoring and optimization strategies are essential for a good position on search engine results pages.
Organic and paid search results
However, optimizing a website for the search results page is not enough for a good ranking.
Google can use user behavior to determine whether a page is actually relevant for the search engine: if a visitor pauses on the page for a few seconds and then moves to the next result, this is a bad sign.
However, if the visitor activates other pages of the homepage and clicks on them, this has a positive effect.
If you want to optimize your search results, analyze in advance what exactly is being searched for and how your visitors behave: Do your users find what are they looking for? Or do they jump off again? You can analyze the behavior of your visitors with Google Analytics, for example.
How do I get into the SERPs? The search results may look different for each query, but they all consist of the same three building blocks:
- Paid advertising (search engine advertising)
- Organic results
- Search results page properties
Below we take a closer look at each of these dots and explain how they might appear there.
Paid Advertising
Paid search results appear before and sometimes after regular results.
Both types of results are practically indistinguishable. The only real difference is that paid ads are marked as such.
Paid advertising works on a pay-per-click (PPC) basis, meaning advertisers bid on keywords and pay Google for each click.
The highest bidders usually get the highest SERP ranking, although Google also considers other factors such as ad relevance and click-through rate. If you want to appear in paid advertising, you have to pay for it.
Organic results
Organic search results are pages from the Google index.
Since there are often thousands of SERPs results, Google sorts them by hundreds of ranking factors. As a result, the most relevant and high-quality pages end up on the first page of search results.
No one knows all of the Google ranking factors, but we do know some of them. For example, we know that the number of backlinks per page is important. Typically, Google SERP will return the usual results by showing the title, URL, and descriptive snippet.
You can tell Google what to display on SERPs by providing the page's title tag, URL, and meta description.
While Google almost always displays a hard-coded title tag in the SERPs, it often chooses something other than a meta description for a snippet.
With structured data pages, Google shows extended descriptions in addition to the normal SERPs results.
If you want to show up in regular search results, you need to focus on creating the best and most relevant result for your query. You also need to make sure that Google can index your pages and that they are optimized for search.
Organic search results can be influenced by search engine optimization. In this case, influence means optimizing your page based on search engine ranking factors.
The implemented measures can be roughly divided into the following two areas:
- On-page optimization:
Includes all measures that are carried out on the page itself. This includes internal link structure, keyword content optimization, pagination, robots.txt, download speed, and redirects.
- Off-page optimization:
This includes all measures that are carried out outside of the page, ie strengthening the page from the outside or making the offer better known. External measures such as link building and the use of social media such as Facebook, LinkedIn, Pinterest, or Twitter.
How these measures are implemented depends on the industry, the goals, the product, the size of the company, and the website. For example, local optimization ( local SEO ) requires different approaches than optimization on a national level. The scope of the measures and their duration depends on these factors.
Regardless of these factors, the fact that SEO is an ongoing process that never ends is undisputed. Some basic SEO measures may have been taken to make the page technically "clean" and therefore easy for the search engine to read.
But only when maintaining websites. For example, ignorance in creating editorial content can cause many problems for a website. Therefore, regular monitoring and coordination by experienced SEO consultants are required.
Importance of SERPs for search engine optimization
A better position in the SERPS compared to direct competitors is the main goal of SERPs search engine optimization.
To get as much traffic as possible through good rankings on your own website, a page must deliver the best and most relevant results, both technically and in terms of content. In addition, the credibility of the website and its links play an important role.
However, ranking is not the only factor in determining a high CTR. When your search snippets have a meaningful title and a short description, website owners are likelier to draw users' attention to the SERP snippets.
Ideally, such a SERP snippet should contain a hint to click.
Therefore, SERP snippet optimization is an important part of search engine optimization and an important part of on-page optimization.
Finally, in most cases, the landing page meta title and meta description are used by search engines for the title and description in the SERPs snippets.
SEO marketers focus on the top ten in the SERPs because 90 percent of users' clicks are shared between them. An optimized snippet increases the likelihood that users will see the result, which increases the click-through rate.
By increasing the number of AdWords ads to four ad units, Google has intensified the battle for top positions in organic search results.
Due to the growing importance of using the mobile Internet, the search results are also adapted to the needs of mobile users.
Mobile searches in the future may show apps or gadget links in the search results, not just on the website results.
Since July 2015, Google has been no longer just a search results provider, but a service provider. At the same time, the index is constantly being expanded to provide individual results tailored to the users and their current situation.
Why is SERPs optimization important for SEO? Most people click results on the first page of the SERPs and rarely visit the second page. This is why everyone wants to be featured on the first page of Google. If you're on the second page or higher, you're practically invisible.
However, first-page rankings do not always mean high traffic for a variety of reasons. Firstly, most of the usual clicks are in the first positions, secondly, paid results often lower organic search rankings.
For example, Google displays four paid ads above regular search results for “buy a car online”. Because of this, 39% of all clicks go to paid results. Third, Google displays features in the SERPs that respond to a query in the search results.
Direct Answers and Rich Snippets in the SERPs
Search engine results are also known as snippets.
These are the title, descriptions, and URLs contained in the SERPs. If a user clicks on such a fragment, he will be redirected to the desired page. Google now also plays snippets with images and other additional information such as ratings.
In this case, these are "enhanced snippets". Google uses markup to display this additional data. These are additions to HTML source code that allow machines to read and process structured data.
Paid search terms are flagged as ads—there are two types of paid results. Paid results are not the result of algorithms, indexing, and crawling. Companies pay search engine providers money for their appearance.
These measures are part of search engine marketing and are also referred to as search engine advertising. The corresponding advertising program is called Google Ads.
Search engines use the search term to decide whether and how much to show paid ads before launching the organic search. The scheme for regular snippets is as follows: the title is blue, the URL is blue, and the description is black and gray.
What are Direct Answers? Direct response is, as the name suggests, a direct response to the user's query and will appear at the top of the search results under the paid ads.
Google exemplifies this response when the search engine believes that a webpage's content answers the user's search query. The direct answer is also referred to as the "answer box" or "position 0" and "recommended snippet" among the SERPs.
Many companies have wanted to rank 0 for this position since Google introduced it in 2015. The ranking in the answer box also affects voice search.
There are three different types of these response fields: paragraph responses, list responses, and table responses.
Over the past month, the percentage of direct replies to all searches has increased by 1.4% and now by more than 13%.
Here are some other key ideas we offer about mobile search results:
- 23.08% of search results on page 1 contain at least 1 AMP result.
- 3.90% of all organic results are AMP (SERPs with at least one AMP).
- Ads appear in 30.90% of search results on the first page.
- Rich cards appear in 20.90% of search results.
- 45.89% of search results contain links to pages.
Direct Answers is one of the advanced search integrations that Google uses to provide users with the information they are looking for without having to click on the result. In most cases, they appear above the regular search results list.
Advanced search integrations are the "little siblings" of universal search integrations, so to speak.
To clarify the definition: Direct answers are most commonly used for informative keywords. This means that the user is looking for an answer to the question in the form of information.
The direct answers implied here are not the information fields that appear in searches such as "weather in Paris". These are also direct answers in the broadest sense, but not selected snippets that you can tweak because the sources for them are generally Freebase, Wikipedia, Knowledge Graph, etc.
What are rich snippets in the SERPs?
In search engine technology, additional small snippets of website content on search engine results pages (SERPs) from search engines such as Google, Yahoo, and Bing are referred to as rich snippets.
With these advanced snippets, users can see in advance whether the web pages listed in the search results are relevant for future searches. The use of rich descriptions of web pages is intended to help users with their search queries.
Unlike the regular snippets, which appear as short pieces of text information below the relevant search results, these extensions contain additional simple informational additions to the search results, e.g. B. star ratings or product prices of the respective website.
With extended snippets, the webmaster can display additional values on his web pages. These meanings are often referred to as semantics. The trend of using such codes has been around for a long time and has been discussed worldwide under the heading Semantic Web.
Conclusion
In online marketing and search engine optimization, many changes to the search engine results page are viewed critically.
This is especially true for reducing the number of regular search results in the first SERPs and the continuous introduction of paid ads and direct answers.


Comments
Post a Comment